Table of contents
Best SAST Tools: Top 10 Solutions Compared
What are static application security testing (SAST) tools?
SAST tools automatically scan the source code of an application. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities before deployment. SAST tools perform white-box testing, which involves analyzing the code based on inside knowledge of the application. SAST offers granularity in detecting vulnerabilities, providing an assessment down to the line of code.
Enterprises often use SAST tools in combination with software composition analysis (SCA tools), dynamic application security testing (DAST) and interactive application security testing (IAST) to extend testing scope.
Key features of SAST tools
Modern SAST tools provide a variety of features designed to integrate security into the development process. These features help developers detect and remediate vulnerabilities efficiently, verifying secure coding practices before deployment.
- Source code analysis: SAST tools analyze the source code, bytecode, or binary code without executing the application. This helps identify code-level vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and buffer overflows.
- Automated scanning: Most tools integrate into the development pipeline and automatically scan code during development, reducing manual security reviews.
- Early integration in SDLC: SAST tools integrate with integrated development environments (IDEs), CI/CD pipelines, and version control systems to ensure issues are caught early, often at the coding stage.
- Customizable rulesets: Many tools allow customization of scanning rules to reflect the organization’s coding standards, frameworks, and threat models.
- Detailed deporting: These tools provide detailed reports with vulnerability descriptions, code locations, and remediation guidance, which helps developers quickly address issues.
- Support for multiple languages: SAST tools typically support a wide range of programming languages and frameworks, making them suitable for diverse tech stacks.
- Compliance and standards mapping: Many SAST tools map findings to compliance standards such as OWASP Top 10, PCI-DSS, or HIPAA, helping teams meet regulatory requirements.
Pros and cons of SAST tools
While SAST tools offer significant advantages for identifying security issues early in development, they also come with certain trade-offs.
Pros:
- Early detection of vulnerabilities: SAST tools analyze code before it is compiled or executed, enabling teams to catch security flaws early in the development process. This reduces the cost and complexity of remediation.
- Developer-centric integration: Many tools integrate directly with IDEs, code repositories, and CI/CD pipelines. This allows developers to get real-time feedback and fix vulnerabilities as they code, improving productivity and security awareness.
- Detailed insights and guidance: SAST tools provide comprehensive reports that highlight the location and nature of vulnerabilities, along with remediation suggestions. This helps simplify the debugging and fixing process.
- Customization and scalability: Organizations can tailor scanning rules to match specific coding practices and compliance requirements. Most tools also support large-scale deployments across multiple projects and teams.
- No need for a running application: Since SAST operates on static code, it doesn’t require a live or compiled application, which simplifies integration into early SDLC stages.
Cons:
- False positives: SAST tools can produce a high volume of false positives, which can overwhelm developers and reduce trust in the tool’s findings if not managed properly.
- Limited runtime context: Because they do not execute the code, SAST tools may miss issues that only appear during application runtime, such as those related to environment-specific configurations or runtime data flows.
- Incomplete coverage: SAST is ineffective at detecting vulnerabilities in compiled dependencies or third-party libraries unless combined with other tools like SCA. It also can’t assess dynamic behaviors like authentication flows or session handling.
- Performance overhead: Deep scanning of large codebases can be time-consuming and may slow down development cycles if not efficiently managed or scoped.
Learning curve and maintenance: Effective use of SAST tools often requires tuning and ongoing maintenance to keep rulesets up to date and minimize irrelevant alerts.
Top 10 static application security testing (SAST) tools
Here are some of the leading SAST solutions on the market today, their key features, delivery model and entry level pricing.
1. Mend.io
Mend SAST provides visibility to over 70 CWE types — including OWASP Top 10 and SANS 25 — in desktop, web and mobile applications developed on various platforms and frameworks.
Mend is typically 10 times faster than traditional SAST products and integrates very easily with your existing DevOps environment and CI/CD pipeline. It takes a “remediation first” approach by integrating the automated remediation capabilities of Mend Cure. Vulnerability alerts and remediation pull requests will be listed directly in developers’ normal workflow, providing a more efficient experience for developers than anything else on the market.
Language support:
- C#
- JAVA
- KOTLIN
- PHP
- PYTHON
- RUBY
- GO
- JAVASCRIPT / NODE.JS
- TYPESCRIPT
- GROOVY
- C/C++
- VB.NET
- VISUAL BASIC
- VBSCRIPT
- ASP CLASSIC
- IOS OBJECTIVE C
- SWIFT
- ANDROID JAVA
- COLDFUSION
- PLSQL
- COBOL
- ABAP
- SALESFORCE APEX
- ASP.NET
- JSP
- HTML/HTML5
- SQL
- XML
- XAMARIN
Delivery model: Cloud
Pricing: Annual subscription based on the number of developers.
Learn more about Mend SAST.
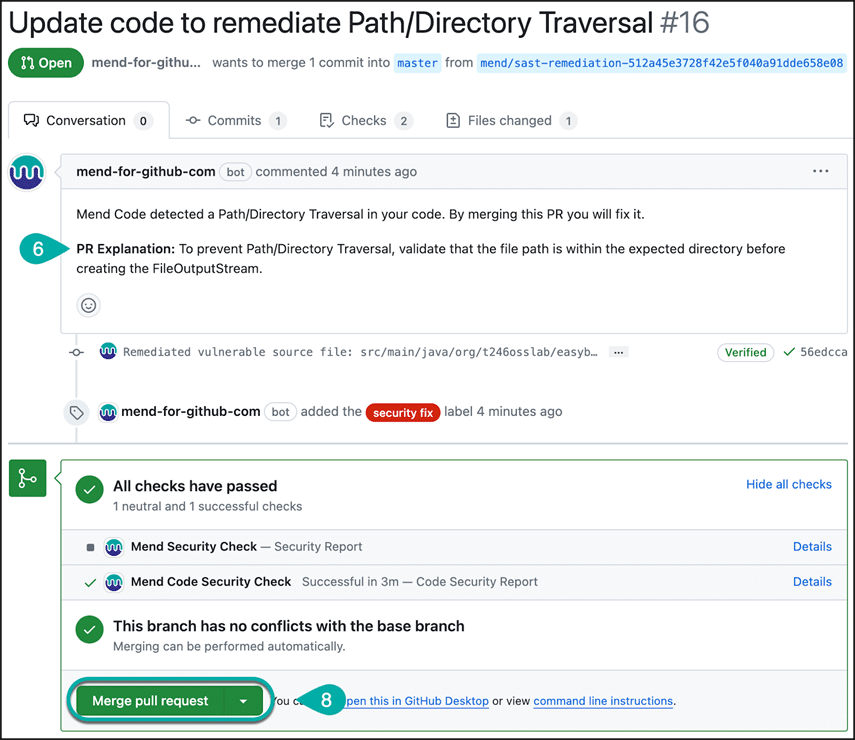
2. SonarQube
SonarQube community edition provides bug and vulnerability detection, code smell tracking, technical debt reviews and remediations, and code quality history and metrics. You can integrate SonarQube with CI/CD and extend its functionality further using more than 60 community plugins.
SonarQube can detect injection flaws and provides real-time IDE notifications. It can also add quality gate and pull request information to the Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) interface.
Language support: Supports 22 languages including C, C#, C++, ABAP, HTML, CSS, Flex, Kotlin, Objective-C, PL/SQL, PHP, Ruby, Swift, Scala, T-SQL, TypeScript, VB.Net, and XML.
Delivery model: On-premises
Pricing: Community—free. Developers—from $500.
3. Xygeni
Xygeni delivers a next-generation SAST solution purpose-built for modern DevSecOps. It goes beyond traditional static code analysis by combining unmatched native detection accuracy and powerful AI-driven AutoFix. This ensures teams focus on vulnerabilities that truly matter while automatically generating secure code fixes.
Xygeni also includes advanced malware detection, spotting threats like backdoors, trojans, and ransomware embedded in first-party code.
Deep IDE and CI/CD integrations embed security into developer workflows without slowing delivery. The platform is part of Xygeni’s broader all-in-one security suite that also covers SCA, secrets detection, CI/CD hardening, IaC scanning, build attestation, and anomaly detection.
Language support: Xygeni SAST supports a wide range of languages and frameworks commonly used in enterprise development, including Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Go, PHP, C#, .NET, and more.
Delivery model: Cloud (SaaS), Hybrid, or fully On-Premise
Pricing: Monthly and Annual subscription based on the number of developers.
4. Veracode
Veracode analyzes application source code and provides automated security feedback via the CI/CD pipeline and IDE. It provides software composition analysis (SCA), security management, audit trail, and reporting.
Veracode offers a manual penetration testing system that allows professionals to analyze the results of security tests to minimize application risk, ensure regulatory compliance, and provide security posture reports. Veracode also enables employees to set security goals for Dev teams, configure risk mitigation workflows, and streamline policy management operations.
Veracode integrates with CI/CD tools including Apache Ant, Docker, Artifactory, Bugzilla, Bamboo, Gradle, Jira, Github, and more, and offers an API for further customization.
Language support: Supports 30 languages including Java (Java SE, Java EE), JDK and OpenJDK, C# and .NET, ASP.NET, C++, JavaScript and TypeScript, PHP, and Scala
Delivery model: Cloud
Pricing: Not publicly available
5. Codacy
Codacy provides insights about the code that go beyond security, including the current code quality of the project and its health over time. It can identify the code’s style and level of complexity, and visually display hotspots indicating quality issues across the codebase. Codacy provides inline annotations in the IDE, 1-click commit suggestions, and reporting that provides visibility into how developers comply with coding standards.
Codacy tightly integrates with GitHub and sends notifications via pull request comments or Slack.
Language support: Supports over 40 languages and frameworks including Kubernetes, Go, Objective-C, Python, Sass, Terraform, Transact-SQL, Swift, and Powershell.
Delivery model: Cloud and on-premises
Pricing: Open-source—free. Pro—$18 per user/mo.
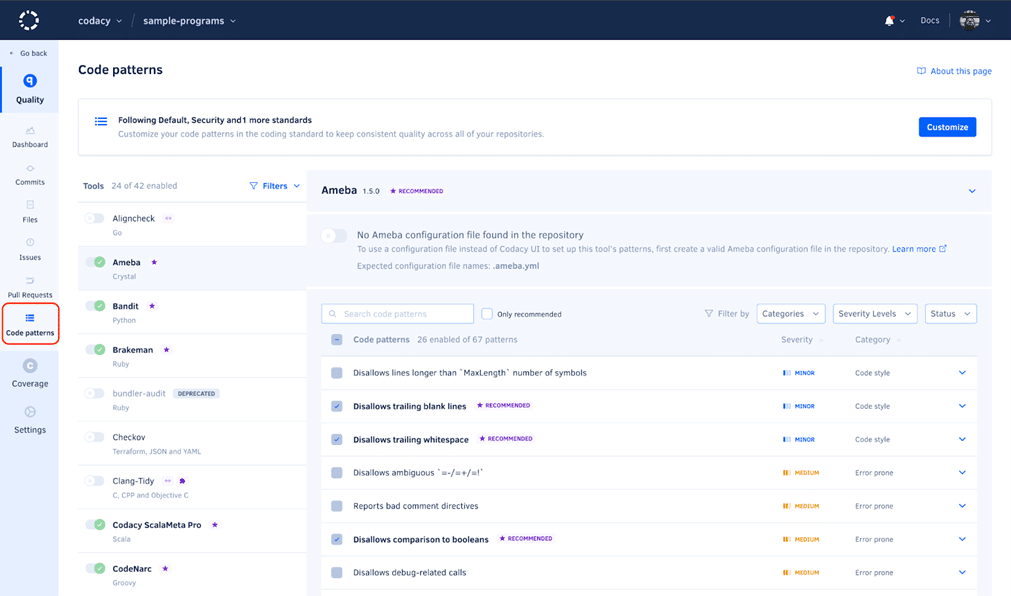
6. Checkmarx CxSAST
Checkmarx CxSAST is a static code analyzer that looks for source code errors and detects security and compliance issues, with no need to build or compile the code. CxSAST constructs a logical graph of the elements and flows of the code and queries this code graph using a list of hundreds of preconfigured queries to identify security vulnerabilities and business logic problems. You can use the CxSAST Auditor tool to configure custom queries for security and functional testing.
CxSAST generates scan results in the IDE (Visual Studio, Eclipse, and IntelliJ), either in an interactive dashboard or as static reports. In each subsequent scan, additional workflow metadata is added to provide context on remediation efforts. The tool’s Open Source Analysis (CxOSA) module enables vulnerability alerts, licensing and compliance management, policy enforcement, and reporting for open-source components.
CxSAST integrates with CI/CD tools including Apache Ant and Maven, Git repositories, JIRA, GitHub, vulnerability management systems like ThreadFix, Bamboo and Jenkins, SonarQube, and source code management tools like TFS.
Language support: Supports over 18 languages including Java, C#, VB.NET, ASP, C/C++, PHP, Ruby, JavaScript, HTML5, PL/SQL, Groovy, and Scala.
Delivery model: Cloud, on-premises, and hybrid
Pricing: Not publicly available
7. Snyk
Snyk Code is a developer-centric static application security testing tool that integrates into IDEs and CI/CD pipelines. It offers real-time scanning without requiring code compilation, providing immediate feedback within the development workflow. The tool emphasizes speed and accuracy, delivering scan results significantly faster than traditional SAST tools.
Language support: Supports 15 languages, including Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Go, C#, C++, PHP, Ruby, Swift, Kotlin, Objective-C, Scala, and Visual Basic.
Delivery model: Cloud-based
Pricing: Free tier available; paid plans start at $25 per user/month.
8. Spectral
Spectral is a static application security testing tool designed for cloud-native applications. It integrates into CI/CD pipelines, providing real-time vulnerability detection and resolution without disrupting the development cycle. Spectral focuses on identifying vulnerabilities early in the development process to reduce technical debt and enhance code quality.
Language support: Supports a wide range of languages commonly used in cloud-native development.
Delivery model: Cloud-based
Pricing: Free tier available, paid plans start at $475/month (billed annually)
9. HCL (previously AppScan)
AppScan is one of the original pioneers in static application security testing (SAST). First launched by Sanctum in the late 1990s, it was later acquired by IBM and became a cornerstone of their AppSec portfolio. Today, AppScan is owned by HCL Technologies, continuing to serve enterprises looking for mature, policy-driven SAST solutions.
AppScan performs vulnerability checks and generates a report that includes remediation suggestions. It provides a range of scanning technologies including SAST, DAST, IAST and Open Source dependency scanning. AppScan provides a “slider” feature that lets you apply the right mix of SAST and DAST to trade off speed vs. coverage.
AppScan enables automation via APIs, or the codeless AppScan Automation Framework that lets you customize integrations to meet specific needs. It provides build-in integrations for popular CI/CD tools.
Delivery model: On-premises and cloud.
Pricing: Not publicly available.
10. OpenText (previously Fortify)
OpenText entered the SAST space through its acquisition of Micro Focus, which had previously acquired HP’s Fortify. With roots tracing back to one of the earliest static analysis engines in the industry, OpenText now offers Fortify as part of its broader cybersecurity portfolio, aimed at large enterprises with complex compliance and security needs.
OpenText Static Application Security Testing provides scalable static analysis to identify vulnerabilities in source code early in the development lifecycle. It integrates with IDEs, CI/CD pipelines, and popular DevOps tools, allowing automated and continuous scanning without requiring code compilation. The platform supports over 30 programming languages and frameworks, enabling broad coverage for enterprise environments.
OpenText offers centralized policy management to enforce secure coding practices and map findings to compliance standards such as OWASP Top 10, PCI DSS, and NIST. The solution also includes customizable rulesets, comprehensive reporting, and integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems to simplify workflows between development and security teams.
Language support: Over 30 languages, including Java, C/C++, C#, VB.NET, JavaScript, Python, Ruby, PHP, Swift, Objective-C, Kotlin, Scala, TypeScript, Go, and SQL.
Delivery model: Cloud and on-premises
Pricing: Not publicly available

Leading SAST solutions compared
| Product Name | Main Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|
| Mend SAST | Fast static code analysis (~10x faster than traditional SAST). Detects 70+ CWE types. Integrates with CI/CD and DevOps tools. Supports automated remediation. | Annual subscription based on number of developers |
| SonarQube | Detects vulnerabilities, code smells, and technical debt. Offers quality gates and PR comments. Community plugins available. | Community: Free. Developer: from $150 |
| Veracode Static Analysis | Static code analysis with CI/CD and IDE integration. Offers manual pen testing, reporting, policy enforcement, and regulatory compliance. | Not publicly available |
| OpenText Application Security Testing | Static code analysis with CI/CD and IDE integration. Supports over 30 languages. Includes centralized policy management, customizable rulesets, compliance mapping (e.g., OWASP, PCI DSS), and SIEM integration. | Not publicly available |
| Codacy | Code quality and security checks with inline suggestions. Hotspot visualization. GitHub and Slack integrations. | Free (OSS). Pro: $15/user/month |
| AppScan | Offers SAST, DAST, IAST, OSS analysis. Includes speed-coverage slider, CI/CD and automation integrations. | Not publicly available |
| Checkmarx CxSAST | Graph-based analysis of source code. No build needed. Includes IDE integration, CI/CD tools, and Open Source Analysis (CxOSA). | Not publicly available |
| Snyk Code | Real-time, compile-free analysis inside IDEs and CI/CD. Fast feedback and developer-friendly. | Free tier. Paid: from $25/user/month |
| Spectral | Real-time SAST for cloud-native apps. CI/CD integration, early detection. | Free tier. Paid: from $475/month (annual billing) |
| DeepSource | Continuous static analysis and Autofix™ suggestions. SCM and CI/CD integration. | Free tier. Paid: from $8/user/month |
What makes a great SAST tool?
Supports shift left
The sooner that a coding flaw is discovered, the faster and easier it is for developers to fix the flaw. With this in mind, it is a best practice to shift security testing, which traditionally was done during the later stages of the software developer lifecycle (the “right” side of the process), to earlier stages of the SDLC (the “left” side of the process). A great SAST tool is able to integrate with existing developer workflow and toolchains to support this shift-left philosophy.
Scans entire repositories
Organizations need to scan all existing code in their repositories. After an initial scan, it’s important to constantly monitor these repositories to identify any issues that might slip through.
Integrates with the CI/CD pipeline
Your CI/CD pipeline could break a build if it experiences security issues. SAST tools that integrate with this pipeline have the capability to immediately warn developers when they’re committing code with security issues, including details of the vulnerability and how to remediate it. They can then take the appropriate action.
Integrating the security tool in the CI/CD pipeline also helps minimize the possibility of an insider adding backdoors within your source code.
Scans fast
Scanning speed is critical in fast-paced DevOps environments. Keep in mind that as soon as a SAST tool is in the critical path of your pipeline, slow scans will hurt developer productivity and may encourage developers to commit less frequently. Or, as frequently happens, developers will find ways to bypass the security tests.
SAST tools can speed up scanning by:
- Caching scanning results
- Running multiple tests in parallel using multiple threads
- Return results promptly
Minimizes false positives
All security-minded teams struggle with false positives. Assessing a false positive wastes time and can also cause alert fatigue. Moreover, it can also distract security personnel, taking their attention away from genuine security issues.
One way to detect false positives is to use a sample application where security issues are known. Scan the application using multiple tools, and choose the SAST tool that achieves the fewest false positives. This process will help you assess how well the tool works with rules and policies. Create a knowledge base of common false positives and share them with your developer teams.
Promotes developer productivity
SAST tools should have a smooth learning curve for developers. Developers should see suggestions about code fixes and library updates alongside security risks. The tool should make it easy for developers to find additional information resources and connect with relevant security communities.
Conclusion
In this article we introduced static application security testing and reviewed several leading tools that can help you identify and resolve security issues early in the development lifecycle. Finally, we provided a few key criteria you can use to evaluate the SAST tool of choice:
- Shift left—how well the tool integrates with developers’ existing workflow and supports security testing at the early stages of code development.
- Scans entire repositories—the tool’s ability to scan all your code and identify issues in legacy code or existing open source components.
- CI/CD integrations—the tool’s support for the technologies in your CI/CD pipeline.
- Scan speed—when SAST becomes part of your build process, scanning speed becomes critical to developer productivity.
- False positives—techniques the tool uses to minimize false positives and assist in issue prioritization.
- Developer productivity—a great SAST tool is one that developers love to work with and can use in their day-to-day activities to minimize security risks.
In summary, SAST is a great addition to your security stack and a key component of DevSecOps strategies. Of course, SAST is not enough to ensure application security, and should be combined with supporting tools such as software composition analysis (SCA), dynamic application security testing (DAST), vulnerability scanning, and container security.
*This article is based on information that is publicly available as of the date of publication and is not intended to represent an independent third-party comparison.